First of all, tokens!
Erc20 is a type of token. The word token has become quite popularized due to the advent of blockchain and an applied form of it - NFTs which means Non-fungible tokens.
In the blockchain world, tokens have different uses. The primary one is as a private digital currency i.e. it can be exchanged for a value. This characteristic is called fungibility. Some tokens however are unique and can not be exchanged, this points to the fact that tokens have other uses. It can be a resource earned; it can represent access rights, it can represent shareholder equity.
Blockchain tokens existed before ethereum; it can however be said that the introduction of the first token standard on Ethereum led to the explosion of tokens.
Tokens differ from Ether (the native currency of Ethereum) in the sense that while ether is an intrinsic action of the Ethereum platform, sending or owning token is not. In simple terms, sending ether is handled at the protocol level while sending and owning token is handled at the smart contract level. In order to create a new token on Ethereum, you must create a new smart contract.
ERC20 name comes from the first standard introduced in November 2015 by Fabian Vogelsteller. It was an Ethererum Request for Comments (ERC) and it was assigned a github issue number 20, hence the name ERC20 token.
ERC20 is a standard for fungible tokens, this means that the unit of ERC20 token are interchangeable and have no unique properties.
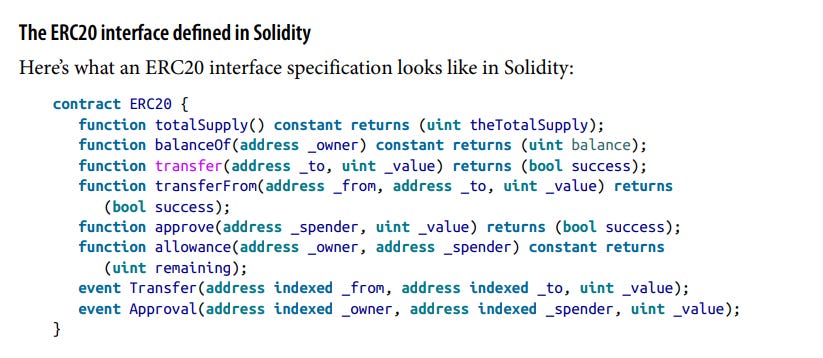
In programming terms, it defines an interface for contracts implementing a token. This means that other tokens building on the standard must implement the number of functions present in the interface. The interface consists of several functions. There are some optional functions too.
The following functions are required
totalSupply: This function returns the total units of this token that currently exist. As the name suggests, it returns the total amount of tokens in supply or circulation. ERC20 tokens can have a fixed or variable supply.
balanceOf: This function will return the ‘token balance’ of a given address.
transfer: This function will transfer a stipulated amount of token to a stipulated address i.e. receiver’s address. The sender is the address that executes this function.
transferFrom: This function takes arguments of sender, recipient and amount. It simply allows transfer of token from the sender to the recipient.
approve
allowance: Given an owner address and a spender address, this function returns the amount remaining that the spender is approved to withdraw from the owner.
Transfer
Approval: This is an event which logs when a call to approve is successful.
Below are the optional functions
name
symbol
decimals
Reference Material
Mastering Ethereum (Building Smart Contracts and DAPPS) by Andreas M. Antonopolus and Dr. Gavin Wood